How Does Osmosis Affect Cells
This Demonstration illustrates the biological concept of tonicity, a mensurate of the osmotic pressure gradient between a jail cell and its surrounding solution. Water can travel across a cell membrane through a process called osmosis, and it e'er moves downward its concentration slope. Therefore, water will travel from a hypotonic solution, which has high water concentration (and low solute concentration) to a hypertonic solution, which has low water concentration (and high solute concentration). This Demonstration shows the move of water for different tonicities.
Details
A solute is a substance dissolved in a liquid, the solvent: water in this Demonstration.
Osmosis is the motility of h2o across a cell membrane. Cells use osmosis to maintain concentration equilibrium (the concentrations of solute inside and exterior the cell are equal). Changing the amount of water allows the cells to achieve equilibrium. When a cell is placed in a solution in which the concentrations are not the same as in the jail cell, the cell undergoes osmosis. The water travels down the concentration gradient from higher water concentration (and lower solute concentration) to lower h2o concentration (and higher solute concentration). In other words, water moves from a hypotonic region to a hypertonic region. Determining which fluid is hypotonic and hypertonic is relative.
When water leaves a cell, it shrinks, which is chosen plasmolysis. When water enters a cell, it expands, which creates turgor pressure on the walls of a establish cell and tin cause the prison cell to explode.
In these snapshots, the solute concentration in the solution exceeds the solute concentration in the cell.
Snapshot one: a hypotonic cell (smaller solute concentration, more water) is initially placed in a hypertonic solution (greater solute concentration, less water)
Snapshot 2: at 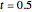 water travels across the cell membrane from the hypotonic to hypertonic location, implying that water leaves the prison cell, causing it to shrink
water travels across the cell membrane from the hypotonic to hypertonic location, implying that water leaves the prison cell, causing it to shrink
Snapshot three: the cell continues to shrink (undergo plasmolysis) until it reaches equilibrium
The contrary would occur if the solute concentration in the cell exceeded the solute concentration in the solution.
Special thanks to the University of Illinois NetMath Program and the mathematics department at William Fremd High School.
References
[1] N. A. Campbell et al., AP Edition Biology, eighth ed., New York: Pearson/Benjamin Cummings, 2008.
[2] Hartnell Higher. "Hartnell College Biology Tutorials." (May 25, 2013) world wide web.hartnell.edu/biology-tutorials.
How Does Osmosis Affect Cells,
Source: https://demonstrations.wolfram.com/EffectsOfCellAndSolutionConcentrationsOnOsmosis/
Posted by: myersmarder.blogspot.com



0 Response to "How Does Osmosis Affect Cells"
Post a Comment